Genistein inhibits high fat diet-induced obesity through miR-222 by targeting BTG2 and adipor1
Abstract
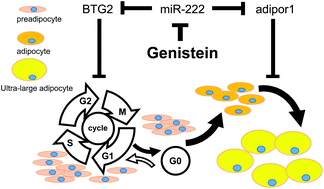
Obesity and diabetes mellitus have become major health problems worldwide. In recent years, genistein has been found to be capable of inhibiting obesity and alleviating insulin resistance. However, the molecular mechanism of genistein against obesity is still not fully understood. In this study, we used 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and obese mice as models to explore the molecular mechanism of genistein against obesity. We found that genistein can inhibit obesity and downregulate the expression of miR-222 in mouse adipose tissue. In 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, treatment with miR-222 inhibitor or genistein reduced the expression of miR-222 and promoted lipid decomposition, while miR-222 treatment increased the expression of miR-222 and inhibited lipolysis. Moreover, the dual-luciferase reporter assay system confirmed that BTG2 and adipor1 are the target genes of miR-222. Experiments conducted in vitro and in vivo suggest that genistein may regulate lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue of obese mice by regulating the expression of miR-222 and its target genes, BTG2 and adipor1. Our findings provide a new epigenetic mechanism underpinning the ability of genistein to resist obesity. These results may provide a reference point for the dietary treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...