On the arrangement of chromophores in light harvesting complexes: chance versus design
Abstract
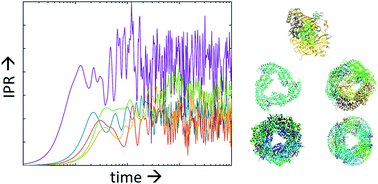
We used a homogeneous computational approach to derive the excitonic Hamiltonian for five light harvesting complexes containing only one type of chromophore and compare them in terms of statistical descriptors. We then studied the approximate exciton dynamics for the five complexes introducing a measure, the (averaged and time-dependent) inverse participation ratio, that enables the comparison between very diverse complexes on the same ground. We find that the global dynamics are very similar across the set of systems despite the variety of geometric structures of the complexes. In particular, the dynamics of four out of five light harvesting complexes are barely distinguishable with a small variation from the norm seen only for the Fenna–Matthews–Olson complex. We use the information from the realistic Hamiltonians to build a reduced model system that shows how the global dynamics are ultimately dominated by a single parameter, the degree of localization of the excitonic Hamiltonian eigenstates. Considering the physically plausible range of system parameters, the reduced model explains why the dynamics are so similar across most light harvesting complexes containing a single type of chromophore regardless of the detailed pattern of the inter-chromophore excitonic coupling.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Quantum effects in complex systems


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...