Atomic layer deposition and electrospinning as membrane surface engineering methods for water treatment: a short review
Abstract
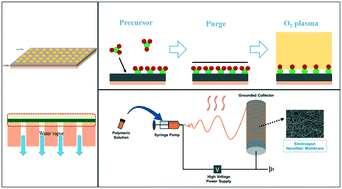
With the development of water purification, membrane processes have drawn attention because of their separation efficiency. However, low rejection efficiency and flux decline driven by membrane fouling remain as challenges. Accordingly, the surface modification of membranes has been widely adopted to enhance membrane processes. For example, the conventional method of sol–gel coating has been mostly used to form a functional top layer that can prevent the accumulation/adsorption of foulants. This conventional method is limited to designing the physico-chemical properties of membranes in a precise manner to achieve an enhanced membrane performance. One advanced method is atomic layer deposition, in which a uniform metal oxide layer is coated at the atomic level. Because of its precise control of the metal oxide layer thickness, it has been mainly applied for tuning the pore structure and/or surface hydrophilicity of membranes. It consequently enhances the rejection efficiency and alleviates fouling by engineering the membrane surface chemistry. The fabrication of an electrospun nanofiber via electrospinning is another approach that has been applied to modify the physico-chemical properties of membranes. It engineers the surface chemistry of membranes (e.g., hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity and surface roughness) by integrating a specific nanomaterial into the electrospun nanofiber. Electrospinning enables porosity tuning by controlling the variations of the fabrication protocol. Despite many studies on membrane surface modification, review articles on the technological progress and the challenges encountered by these functionalization methods are lacking. This review article provides the following: i) an introduction of the nanomaterials (e.g. graphene based nanomaterials, carbon nanotubes and titanium dioxide) and three methods for surface modification; ii) a systematic summary of their application in ALD and electrospinning, and in membrane processes for water treatment; and consequently iii) insight into the technological challenges and future perspectives for their wider application in the membrane industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...