Binding ability of arsenate towards Cu2+ and Zn2+: thermodynamic behavior and simulation under natural water conditions†
Abstract
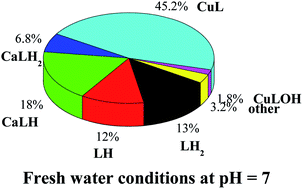
A study on the sequestering ability between arsenate, AsO43−, and Cu2+ and Zn2+ in aqueous solution is reported. The results of the elaboration of potentiometric data include only species with 1 : 1 metal to ligand ratio for Cu2+–arsenate system, namely CuLH2, CuLH, CuL, and CuLOH (L = AsO43−). For the Zn2+–arsenate system, a speciation model with only two species with both 1 : 1 and 1 : 2 metal to ligand ratios was obtained, namely ML and ML2. Spectrophotometric titrations were also employed in the study of the Cu2+–AsO43− system, and the results of the analysis of experimental data fully confirmed potentiometric ones. The potentiometric titrations were performed under different conditions of temperature (288.15 ≤ T/K ≤ 310.15, at I = 0.15 mol L−1) and ionic strength (0.15 ≤ I/mol L−1 ≤ 1 in NaCl). The dependence of formation constants of the complex species on ionic strength and temperature was also evaluated, as well as the enthalpy and entropy change values were obtained. Laser desorption mass spectrometry (LD MS) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) were exploited to confirm Cu2+–AsO43− and Zn2+–AsO43− complex formation and to determine both their composition and structural characteristics. Simulation of speciation profiles under natural water conditions was performed. The sequestering ability of arsenate towards Cu2+ and Zn2+ was quantified under different conditions of pH, temperature and ionic strength, typical of several natural waters. Examples of arsenate distribution under seawater and freshwater conditions were reported.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...