A novel Mg(OH)2 binding layer-based DGT technique for measuring phosphorus in water and sediment†
Abstract
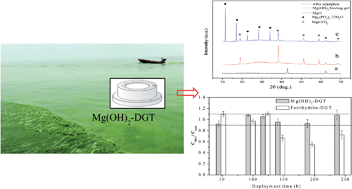
Diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) have gained wide attention for in situ measurement of reactive phosphorus species (PO4) in natural water, sediments and potentially soils. In this study, a novel Mg(OH)2 binding gel was formed using magnesium hydroxide obtained by in situ hydration of calcined magnesium oxide. Laboratory scale experiments showed that the novel Mg(OH)2 gel had a homogeneous dispersion of fine particles of Mg(OH)2 with a particle size of 2–5 μm. With 10 mL of 2.0 mol L−1 NaOH as the eluting agent, the optimal elution efficiency of PO4 on the Mg(OH)2 gel was 72 ± 5%. There were linear relationships between the accumulated PO4 mass and the applied PO4 concentration (0.1 to 20 mg P per L), time (0 to 24 h) and temperature (22 to 40 °C). The capacity of the Mg(OH)2 binding layer was determined to be 99.5 μg P per disc. Tests in synthetic seawater, Chaohu Lake and Yihai Pond confirmed that Mg(OH)2-DGT was able to accurately measure phosphorus up to 10 days. This was indicated by the good agreements between the concentrations measured by DGT (CDGT) technology and by an ex situ chemical method in solution (Csoln), with a CDGT/Csoln ratio between 0.91 and 1.09.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...