Techno-economic analysis of capacitive and intercalative water deionization†
Abstract
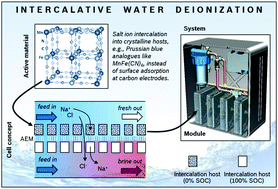
We conduct a techno-economic analysis of electrochemical water deionization technologies. The objective of the analysis is to compare cost, volume, and energy consumption of membrane capacitive deionization (mCDI) to intercalative deionization techniques. Here, we first explore the concept of hybrid capacitive deionization (HCDI), i.e., a cation intercalation electrode paired with an activated carbon capacitive electrode. Then we explore in detail a novel device concept, fully intercalative water deionization (IDI), which relies entirely on the cation intercalation principle. The intercalation host materials in our study are Prussian blue analogs (PBAs), e.g., NiFe(CN)6 or CuFe(CN)6, that offer ∼3–5× higher gravimetric salt removal capacities than typical activated carbon. Our analysis shows that IDI should be superior to mCDI in module cost, volume, and energy efficiency, despite a more complex module architecture. Making careful assumptions on material costs, we provide a cost breakdown for mCDI, HCDI, and IDI modules and show that IDI is the only concept that is not dominated by ion exchange membrane costs. The environmental impact of electrochemical water deionization is illustrated by estimating the carbon footprint of currently installed reverse osmosis capacity in different world regions and comparing it to the respective carbon footprint of mCDI, HCDI, and IDI at similar capacity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...