Fe-Doped Co–Mo–S microtube: a highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting in alkaline solution†
Abstract
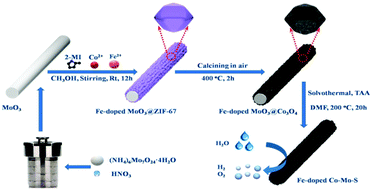
Fe-Doped Co–Mo–S microtubes were successfully synthesized through a multistep synthetic route, employing MoO3 microrods as the sacrificial template, Co(NO3)2·6H2O and Fe(SO4)2·7H2O as the metal sources, 2-methylimidazole (2-MI) as the ligand and thioacetamide (TAA) as the S2− ion source. The as-prepared products were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), (high-resolution) transmission electron microscopy (TEM/HRTEM) and HAADF-STEM-EDS elemental mapping. Experiments showed that the as-obtained Fe-doped Co–Mo–S microtube catalyst demanded overpotentials of ∼105 and 268 mV to afford the current density of −10 mA cm−2 for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and 10 mA cm−2 for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) with a durability of 60 h in 1.0 M KOH solution, respectively. In a two-electrode water-splitting device, the as-prepared Fe-doped Co–Mo–S microtubes acted as both anode and cathode simultaneously. To deliver a current density of 10 mA cm−2, a cell voltage of 1.605 V was required in 1.0 M KOH solution. After continuously catalyzing the overall water splitting for 60 h, the overpotential hardly changed, implying remarkable long-term stability. Obviously, the present Fe-doped Co–Mo–S microtubes have potential applications as bifunctional catalysts for electrochemical water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...