Near-infrared-emitting AIE multinuclear cationic Ir(iii) complex-assembled nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
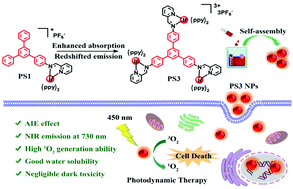
Near-infrared (NIR) emission and impressive singlet oxygen (1O2) generation ability are highly desirable but remain difficult to realize as aggregation-induced emission (AIE) photosensitizers (PSs). Herein, mono- and tri-nuclear NIR AIE cationic Ir(III) complexes and their corresponding self-assembled nanoparticles (NPs) without any surfactants or adjuvants were designed and synthesized by integrating rigid 1,3,5-triphenyl benzene as an extended π-conjugation bridge. The pure NPs exhibit multiple merits of stronger NIR emission, higher 1O2 production capacity, better water solubility and negligible dark toxicity compared with the Ir(III) complexes. Notably, the AIE PS3 NPs possess bright NIR emission at 730 nm, suitable spherical sizes below 100 nm, favorable cellular uptake and superior phototoxicity (IC50 = 1.4 × 10−6 M). These are the first pure NIR-emitting multinuclear Ir(III) complex NPs obtained by self-assembly that exhibit excellent cell imaging and photodynamic therapy (PDT) performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...