Dinuclear phosphorescent rhenium(i) complexes as potential anticancer and photodynamic therapy agents†
Abstract
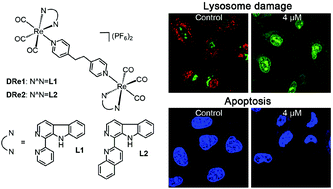
Chemotherapeutic agents that affect lysosomal functions represent a promising strategy for selective tumor therapy and overcoming drug resistance. In this work, two dinuclear phosphorescent rhenium(I) tricarbonyl complexes (DRe1 and DRe2) containing carboline derivatives have been synthesized, characterized and explored as potential chemotherapeutic and photodynamic therapy agents. The two dinuclear rhenium(I) complexes have good intrinsic phosphorescence properties and can label the lysosomes in cancer cells. Both dinuclear rhenium(I) complexes show potent anticancer activities toward several tested cancer cells. Moreover, they also have marked inhibitory activities against cisplatin-resistant human lung carcinoma cells (A549R), with complex DRe2 displaying 16-fold higher activity than cisplatin. Mechanism studies reveal that complex DRe2 can induce cancer cells to overproduce reactive oxygen species (ROS), including superoxide anion radicals, which leads to lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) and subsequent cell apoptosis. Additionally, both DRe1 and DRe2 display significant phototoxicity under light (425 nm) irradiation in A549 cells, with phototoxicity index values of 60.8 and 41.8, respectively. Therefore, these two dinuclear organometallic rhenium(I) tricarbonyl complexes are potential anticancer agents for combined chemo-photodynamic therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...