Synthesis of a series of novel In(iii) 2,6-diacetylpyridine bis(thiosemicarbazide) complexes: structure, anticancer function and mechanism†
Abstract
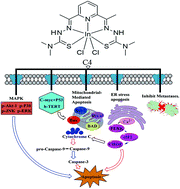
The anticancer function and anticancer mechanism of indium (In) complexes still remain mysterious to date. Furthermore, it is greatly challenging to design a multi-functional metal agent that not only kills cancer cells but also inhibits their invasion and metastasis. Thus, to develop novel next-generation anticancer metal agents, we designed and synthesized a series of novel In(III) 2,6-diacetylpyridine bis(thiosemicarbazide) complexes (C1–C4) for the first time and then investigated their structure–activity relationships with human urinary bladder cancer (T-24) cells. In particular, C4 not only showed higher cytotoxicity to cancer cells and less toxicity toward normal cells relative to cisplatin but also inhibited cell invasion and metastasis of T-24 cells. Interestingly, C4 acted against T-24 cells exhibiting multiple mechanisms: (1) arresting the S-phase of cell cycle via regulation of cytokine kinases, (2) activating the mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum-stress-mediated cell death, PERK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK) cell signaling pathways, and (3) inhibiting the expression of telomerase via the regulation of c-myc and h-TERT proteins. Our results suggested that C4 may be developed as a potential multi-functional and multi-targeting anticancer candidate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...