Uniaxial thermal expansion behaviors and ionic conduction in a layered (NH4)2V3O8†
Abstract
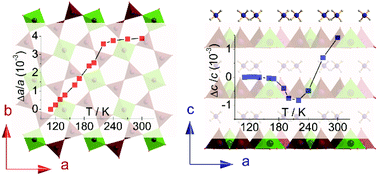
The zero/negative thermal expansion (ZTE/NTE), which is an intriguing physical property of solids, has been observed in a few families of materials. ZTE materials possess practical applications in specific circumstances such as space-related applications, engineering structures and precision instrument. Generally, NTE materials are used as additives to form a composite of the ZTE material with positive thermal expansion material. It is still a tremendous challenge to design new families of ZTE/NTE materials. Herein, we presented a temperature-dependent single crystal structure analysis in 110–300 K for a layered (NH4)2V3O8, which crystallizes in a tetragonal space group P4bm and comprises mixed valence [V3O82−]∞ monolayers and NH4+ residual in the interlayer spaces. Along the c-axis, (NH4)2V3O8 demonstrated uniaxial expansion behaviors, i.e., ZTE with αc = −1.10 × 10−6 K−1 in 110–170 K and NTE with αc = −16.25 × 10−6 K−1 in 170–220 K. Along the a-axis, (NH4)2V3O8 exhibited ZTE with αa = + 2.06 × 10−6 K−1 in 240–300 K. The mechanisms of ZTE and NTE were explored using structural analysis. The conduction of NH4+ ions in the interlayer space was studied, indicating that the conductivity rapidly rises with the expansion of interlayer space at temperatures of >293 K. This study discloses that layered vanadates are promising ZTE/NTE materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...