An 8-hydroxyquinoline–proline hybrid with multidrug resistance reversal activity and the solution chemistry of its half-sandwich organometallic Ru and Rh complexes†
Abstract
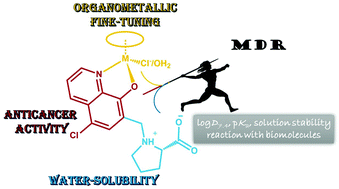
Herein the design and synthesis of a new 8-hydroxyquinoline derivative, (S)-5-chloro-7-((proline-1-yl)methyl)8-hydroxyquinoline (HQCl-Pro), with good water solubility and multidrug resistance reversal activity are reported. In this work the proton dissociation processes of HQCl-Pro and its complex formation with [Rh(η5-C5Me5)(H2O)3]2+, [Ru(η6-p-cymene)(H2O)3]2+ and [Ru(η6-toluene)(H2O)3]2+ were investigated by the combined use of pH-potentiometry, UV-visible spectrometry and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Our results revealed the prominent solution stability of the complexes in all cases. The lipophilicity of the complexes increased with the chloride ion concentration, and the complexes showed moderate log D values (−0.8 to +0.4) at pH 7.4 at all tested Cl− concentrations. The formation of mixed hydroxido complexes from the aqua complexes was characterized by relatively high pKa values (8.45–9.62 in chloride-free medium). Complexation processes are much slower with the Ru(η6-arene) triaqua cations than with [Rh(η5-C5Me5)(H2O)3]2+. Both the pKa values and H2O/Cl− exchange constants of the Ru-complexes are lower by 0.5–1.0 orders of magnitude than those of the Rh analogue. Arene loss (p-cymene and toluene) and oxidation were found in the case of Ru-complexes when an excess of HQCl-Pro and aromatic (N,N) bidentate ligands was added. The cytotoxicity and antiproliferative effect of HQCl-Pro and its complexes were assayed in vitro. In contrast to the structurally familiar 8-hydroxyquinoline, HQCl-Pro and its Rh(η5-C5Me5) complex were somewhat more effective against drug resistant Colo 320 adenocarcinoma human cells compared to the drug sensitive Colo 205 cells. The Ru- and Rh-complexes showed a similar metal uptake level after 4 h, while a longer incubation time resulted in higher cellular Rh concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...