Facile synthesis of Mn-doped NiCo2O4 nanoparticles with enhanced electrochemical performance for a battery-type supercapacitor electrode†
Abstract
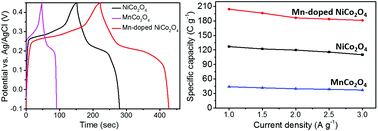
We report the synthesis of manganese-doped nickel cobalt oxide (Mn-doped NiCo2O4) nanoparticles (NPs) by an efficient hydrothermal and subsequent calcination route. The material exhibits a homogeneous distribution of the Mn dopant and a battery-type behavior when tested as a supercapacitor electrode material. Mn-doped NiCo2O4 NPs show an excellent specific capacity of 417 C g−1 at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1 and 204.3 C g−1 at a current density of 1 A g−1 in a standard three-electrode configuration, ca. 152–466% higher than that of pristine NiCo2O4 or MnCo2O4. In addition, Mn-doped NiCo2O4 NPs showed an excellent capacitance retention of 99% after 1000 charge–discharge cycles at a current density of 2 A g−1. The symmetric solid-state supercapacitor device assembled using this material delivered an energy density of 0.87 μW h cm−2 at a power density of 25 μW h cm−2 and 0.39 μW h cm−2 at a high power density of 500 μW h cm−2. The cost-effective synthesis and high electrochemical performance suggest that Mn-doped NiCo2O4 is a promising material for supercapacitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...