Growth of InZnP/ZnS core/shell quantum dots with wide-range and refined tunable photoluminescence wavelengths†
Abstract
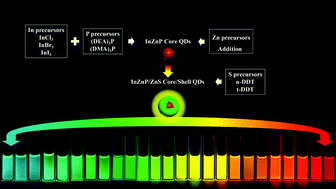
Owing to their environmentally friendly characteristic, InP-based quantum dots (QDs) show great potential in various fields as an alternative to Cd-based QDs. However, the current mainstream synthesis process, the (TMS)3P-based injection method, still faces many challenges, such as the high cost of (TMS)3P and complex temperature control. In contrast, the solvothermal method is considered to be more feasible and reproducible. Despite its potential advantages, little has been done to understand how the precursors influence the synthesis of InP QDs using the solvothermal method. In this research, InZnP/ZnS QDs were synthesized using practical phosphorus precursors (DEA)3P or (DMA)3P. Through the feasible regulation of zinc, indium, phosphorus and sulfur precursors, the band gap of the QDs could be widely and accurately tuned, and a much wider photoluminescence wavelength ranging from 484 nm to 651 nm could be achieved. Furthermore, InI3 and InBr3 contributed to the blueshift in the PL wavelengths, and the combination of (DEA)3P, (DMA)3P, n-DDT and t-DDT refined the PL wavelength with a small tuning gap of 5 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...