Naproxen platinum(iv) hybrids inhibiting cycloxygenases and matrix metalloproteinases and causing DNA damage: synthesis and biological evaluation as antitumor agents in vitro and in vivo†
Abstract
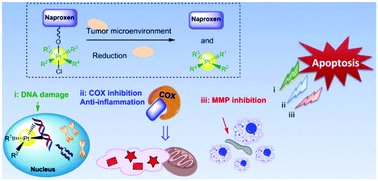
Cycloxygenases (COXs) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the tumor microenvironment (TME) are tightly related to the progression of cancers. Here, naproxen as a potent inhibitor of both COX and MMP was combined with platinum(IV) to construct hybrids as antitumor agents. Compound 2 with comparable or even superior activities to that of cisplatin, oxaliplatin, and carboplatin, great potential for reversing drug resistance, and superior tumor targeting properties was screened out as a lead compound. Moreover, compound 2 possessed potent tumor growth inhibition capability in vivo, which was comparable to that of oxaliplatin, and displayed rather lower side effects than the platinum(II) reference drugs. The naproxen platinum(IV) complex could easily undergo reduction and liberate the platinum(II) complex and naproxen as well as exert a multifunctional antitumor mechanism: (i) the liberated platinum(II) fragment would cause serious DNA injury; (ii) naproxen would inhibit COX-2 and decrease tumor-associated inflammation; and (iii) the naproxen platinum(IV) complex exhibited remarkable MMP-9 inhibition in tumor tissues. These antitumor functions can help reduce the growth and metastasis of malignancy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...