Electronic influence of substitution on the pyridine ring within NNN pincer-type molecules†
Abstract
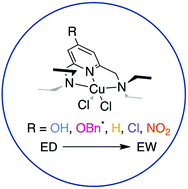
Pincer molecules are of increasing interest due to the modular nature of modification and range of reactivity observed when coordinated to metal ions. A subset within the family of pincer molecules use a pyridine group to bridge the outer two arms as well as provide a N-donor atom for metal binding. While the arm appendages have been studied extensively, little research has been conducted on the electronic effects of the central, substituted pyridine systems. Therefore, a series of NNN pincer-type ligands with substitution on the 4-position of the pyridine ring with –OH, –OBn, –H, –Cl, and –NO2 functional groups were synthesized and characterized through NMR spectroscopy and ESI-HRMS. Each pincer was metalated with Cu(II) salts and evaluated through X-ray diffraction analysis, cyclic voltammetry, and density functional theory analysis. The results indicate that the relatively unstudied –OBn group demonstrates both electron-withdrawing (XRD bond lengths) and electron-donating (NMR spectroscopy) properties. The –NO2 pincer ligand shows a redox event within experimental windows evaluated, in contrast to the other congeners studied. In addition, electron-donating groups increase the electron density around the Cu(II) center based on DFT studies and cyclic voltammetry. These findings can be applied to other pyridine-based pincer systems when considering ligand design and warrants future characterization of 4-position substituted pyridines.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...