NiO nanocomposites/rGO as a heterogeneous catalyst for imidazole scaffolds with applications in inhibiting the DNA binding activity†
Abstract
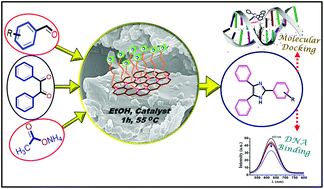
Herein, we report a facile approach to synthesize a new highly versatile heterogeneous catalyst by spontaneous aerial oxidation based on nickel oxide nanocomposites immobilized on surface-functionalized reduced graphene oxide sheets. NiO nanocomposite/reduced graphene oxide (rGO–NiO-NC) is a highly efficient, cost-effective, reusable, selective, and eco-friendly nano-catalyst that does not lose any activity even after five reaction cycles. Nickel loading on the rGO-NiO nanocomposite was found to be 3.3 at%, which contributes to the effective and efficient use of rGO–NiO-NCs as a nano-catalyst for the synthesis of imidazole derivatives. Consequently, a series of imidazole derivatives were synthesized, catalyzed by rGO–NiO-NCs, in 60 min with high yields (86% to 96%) under green conditions. Furthermore, the present synthetic methodology was used for the synthesis of highly aromatic imidazole derivatives (B1–B3) whose calf thymus-DNA binding affinities suggest their superior inhibition ability to displace ethidium bromide (EB), which was further confirmed by molecular docking studies. Additionally, the green chemistry matrix of the synthesis reaction was found to be very close to ideal values, such as carbon efficiency (82.32%), E-factor (0.51), atom economy (77.86%), process mass intensity (1.51), and reaction mass efficiency (66.14%).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...