Synthesis, characterization, kinetic investigation and biological evaluation of Re(i) di- and tricarbonyl complexes with tertiary phosphine ligands†
Abstract
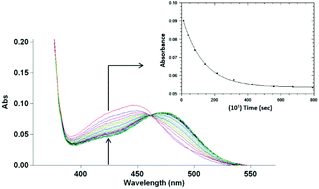
Rhenium(I) di- and tri-carbonyl complexes of the form fac-[Re(CO)3(L,L′-Bid)X] and [Re(CO)2(L,L′-Bid)X2], where X = aqua (H2O), methanol (CH3OH), triphenylphosphine (PPh3), 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA), tricyclohexylphosphine (PCy3) and L,L′-Bid = O,O′ bidentate ligands (tropolone = TropH and 3-hydroxyflavone = FlavH) and N,O bidentate ligands (8-hydroxyquinoline = QuinH, 5,7-chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline = diCl-QuinH and quinoline-2,4-dicarboxylic acid = QuinH2), were synthesized and unambiguously characterized by 1H-, 13C-and 31P-NMR, IR, UV/Vis and micro-analysis. The crystal structures of four complexes, namely fac-[Re(CO)3(QuinH)(H2O)]·H2O (5), fac-[Re(CO)3(Quin)(PPh3)] (11), fac-[Re(CO)3(diCl-Quin)(PPh3)] (12) and [Re(CO)2(Trop)(PPh3)2]·2C6H5CH3 (20) were obtained. Re–P bonding distances for 11 and 12 are 2.4948(8) and 2.4908(8) Å, respectively, indicating the effect of the electron-withdrawing substituents of the diCl-Quin− ligand. The second-order rate constants for the substitutions of methanol at 25.1 °C in fac-[Re(CO)3(L,L′-Bid)(CH3OH)] (L,L′-Bid = Trop, Flav and QuinH) type complexes by different entering phosphine ligands (PPh3, PCy3, and PTA) varied between 7.23(7) × 10−5 and 1.32(3) × 10−3 M−1 s−1 and were found to depend on the coordinated bidentate ligand (in general k1 (QuinH) < k1 (Trop) < k1 (Flav)). The toxicity of fac-[Re(CO)3(QuinH)(PTA)], fac-[Re(CO)3(Trop)(PTA)], fac-[Re(CO)3(Trop)(PPh3)] and fac-[Re(CO)3(Flav)(PPh3)] on the cervical cancer HeLa and epithelial RPE-1 cell lines was then evaluated. Complex fac-[Re(CO)3(Flav)(PPh3)] (16) and fac-[Re(CO)3(Trop)(PPh3)] (13) displayed the highest cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 12.21 ± 0.17 μM and 13.35 ± 0.94 μM, respectively in HeLa cells. Interestingly, a small selectivity towards cancer over non-cancerous cells was observed for these compounds (IC50 = 18.41 ± 3.16 μM and >25 μM in RPE-1 cells).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...