The effect of organosilicon modifier structure on the efficiency of the polybutadiene hydrosilylation process†
Abstract
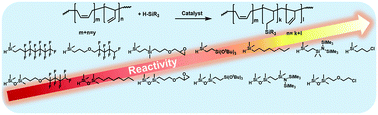
Herein we present a simple catalytic approach to the synthesis of organosilylfunctional polybutadienes. The use of highly active Rh(I) catalysts enabled high conversions of a wide range of organofunctional silicon-based modifiers, which permitted obtaining a library of new functional polymers equipped with attractive silicon-based functional groups. The use of real-time FT-IR spectroscopy allowed us to determine the end-point of the reaction as well as the influence of steric and electronic properties of functional groups on the course of hydrosilylation. In addition, it allowed us to establish the impact of the spacers between a H–Si≡ moiety and the functional group on the reactivity of the synthesized silanes or siloxanes in the polybutadiene hydrosilylation reactions. All products were characterized by NMR spectroscopy and GPC analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...