A Pickering emulsion of a bifunctional interface prepared from Pd nanoparticles supported on silicane-modified graphene oxide: an efficient catalyst for water-mediated catalytic hydrogenation†
Abstract
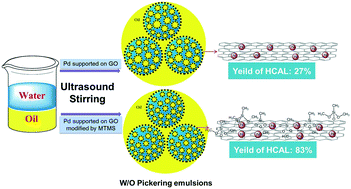
A Pickering emulsion was prepared from Pd nanoparticles supported on organic-silicane-modified graphene oxide (GO-Si), and was used as a highly efficient catalyst for selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde (CAL) in water medium in place of organic solvents. The silicane-modified GO enhanced the lipophilicity of the Pd/GO-Si surface, thus promoting adsorption of CAL at the interface of the Pickering emulsion prepared by Pd/GO-Si. In addition, the lipophilic surface of Pd/GO-Si was beneficial to stabilize the Pickering emulsion of water in oil (W/O). It was found that as the grafting amount of silicane increased from 0.6 to 1.4 g, droplets in the Pickering emulsion of W/O became smaller and denser, which was closely related to catalytic performance for selective hydrogenation of CAL in water medium. The as-prepared Pickering emulsion exhibited high activity and selectivity for hydrogenation of CAL, which was attributed to the bifunctional synergy of the interface of the Pickering emulsion prepared by Pd/GO-Si. Furthermore, compared with the conventional catalytic systems proceeding using organic solvents, the Pickering emulsion prepared by Pd/GO-Si exhibited superior activity under the same reaction conditions. The maximum hydrocinnamaldehyde (HCAL) yield was 83% in 20 min. Moreover, the catalyst demonstrated good recyclability and versatility for selective hydrogenation with various substrates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...