Industrial carbon dioxide capture and utilization: state of the art and future challenges
Abstract
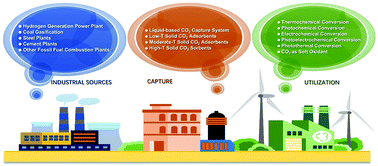
Dramatically increased CO2 concentration from several point sources is perceived to cause severe greenhouse effect towards the serious ongoing global warming with associated climate destabilization, inducing undesirable natural calamities, melting of glaciers, and extreme weather patterns. CO2 capture and utilization (CCU) has received tremendous attention due to its significant role in intensifying global warming. Considering the lack of a timely review on the state-of-the-art progress of promising CCU techniques, developing an appropriate and prompt summary of such advanced techniques with a comprehensive understanding is necessary. Thus, it is imperative to provide a timely review, given the fast growth of sophisticated CO2 capture and utilization materials and their implementation. In this work, we critically summarized and comprehensively reviewed the characteristics and performance of both liquid and solid CO2 adsorbents with possible schemes for the improvement of their CO2 capture ability and advances in CO2 utilization. Their industrial applications in pre- and post-combustion CO2 capture as well as utilization were systematically discussed and compared. With our great effort, this review would be of significant importance for academic researchers for obtaining an overall understanding of the current developments and future trends of CCU. This work is bound to benefit researchers in fields relating to CCU and facilitate the progress of significant breakthroughs in both fundamental research and commercial applications to deliver perspective views for future scientific and industrial advances in CCU.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...