Superconducting behavior of BaTi2Bi2O and its pressure dependence
Abstract
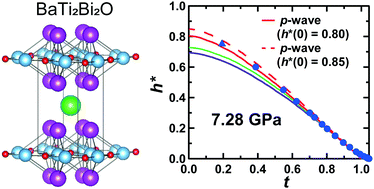
A new superconducting sample, BaTi2Bi2O, was synthesized and characterized over a wide pressure range. The superconducting transition temperature, Tc, of BaTi2Bi2O was 4.33 K at ambient pressure. The crystal structure was tetragonal (space group of P4/mmm (No. 123)), according to the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern at ambient pressure. The XRD pattern was analyzed using the Le Bail method. The magnetic-field dependence of the magnetization at different temperatures was precisely investigated to elucidate the characteristics of the superconductivity. The pressure-dependent XRD patterns showed absence of structural phase transitions up to 19.8 GPa. The superconducting properties of BaTi2Bi2O were investigated under pressure. Tc monotonously increased with the pressure (p) up to 4.0 GPa and saturated above 4.0 GPa. The variations in the Tc–p plot were thoroughly analyzed. The Cooper pair symmetry (or superconducting pairing mechanism) was analyzed based on the magnetic field dependence of the superconductivity at ambient and high pressures, which indicated a sign of p-wave pairing for the superconductivity of BaTi2Bi2O, i.e., topologically nontrivial sign was suggested for BaTi2Bi2O.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...