Aqueous solutions of binary ionic liquids: insight into structure, dynamics, and interface properties by molecular dynamics simulations and DFT methods†
Abstract
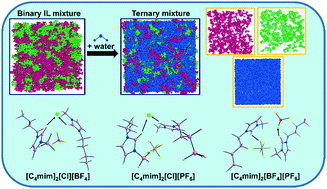
The behavior of aqueous solutions of mixtures of ionic liquids (ILs) is of special interest because of their amphiphilic character, from both a fundamental and application viewpoint. In this work, we conducted molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and density functional theory (DFT) calculations to understand the effect of water on the intermolecular interactions in three IL binary mixtures [C4mim]/[Cl]/[BF4], [C4mim]/[Cl]/[PF6] and [C4mim]/[BF4]/[PF6] containing the well-characterized cation, 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium [C4mim]+ and the anions chloride [Cl]−, tetrafluoroborate [BF4]−, and hexafluorophosphate [PF6]−. The perturbation of the structures in the binary IL mixture by water molecules was analyzed in the bulk and at the liquid/vacuum interface using distribution functions, hydrogen-bond statistics, and density profiles. Interactions between anions and cations change drastically when the IL mixtures are dissolved in water. In particular, anion–water interactions are stronger than anion–cation interactions. H-Bonds are the dominant interactions. They are prevalently electrostatic and strong for the two [Cl]-containing systems in both the water-free and the water-containing systems. The very hydrophobic [C4mim]/[BF4]/[PF6] system gains stability from dispersive interactions and consequently segregates water markedly when admixed. The most probable orientations of IL cations in the bulk and at the vicinity of the interface were examined using bivariate distribution calculations and show [PF6]− segregating to the surface in keeping with its highly hydrophobic nature. DFT calculated structures, energies, dipole moments, global hardness and solvation energies using model ion pairs [C4mim][X] or complexes [C4mim]2[X][Y], with [X/Y]− = [Cl]−, [BF4]−, or [PF6]− are completely consistent with the findings for the bulk.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...