Magnetic compensation and critical behavior in spinel Co2TiO4
Abstract
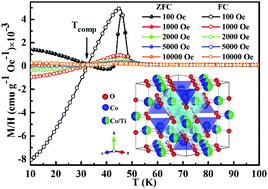
We report studies of the complex magnetic ordering, pressure-induced magnetic properties, large exchange bias (EB), spin-glass (SG), critical behavior, and electron spin resonance (ESR) in spinel Co2TiO4. The magnetic compensation behavior occurs in the vicinity of the compensation temperature Tcomp ∼ 32.5 K (defined as the susceptibility χZFC = χFC = 0), which can be attributed to the behavior that the magnetization of two bulk sublattices balances each other completely. The nature of this unusual case is demonstrated by the spin direction upon applied field and A–B sublattice (site) coupling. Specifically, the values of exchange integrals JAA and JBB play a crucial role at lower and higher temperatures, respectively. It is prominent that intrinsic coercivity Hcj increases by 168% at a pressure of 1000 MPa, from which we illustrate the antiferromagnetic (AFM) transition based on magnetic hysteresis loops M(H) and temperature dependent magnetization M(T) curves. The SG behavior of Co2TiO4 is confirmed by a series of reliable measurements and fitting parameters (τ0, zv), and a large EB field is also found through the asymmetry in the M(H) curve. Besides, the critical behavior of Co2TiO4 is studied initially in our present work, and the critical exponents (β, γ, and δ) indicate long-range ferromagnetic (FM) coupling accompanied by a short-range interaction in Co2TiO4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...