Kinetic investigation of thermal and photoinduced homolysis of alkylated verdazyls†
Abstract
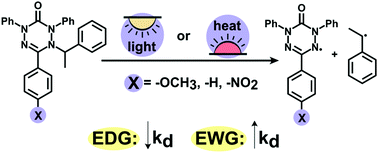
The on-demand generation of stable organic radicals from the precursors can be considered as an essential challenge for the plethora of applications in various fields of science. In this contribution, we prepared a range of N-(methyl)benzyl derivatives of 6-oxoverdazyl via atom transfer radical addition from moderate to high yields and studied their thermal- and photo-initiated homolysis. The kinetics of homolysis was measured, and the dissociating rate constant kd, activation energy Ea and frequency factor A were estimated. Variation of the substituent at the C3-position of the verdazyl ring was successfully applied for fine-tuning the homolysis rate: the value of kd was higher for alkylverdazyls with electron-withdrawing groups, e.g., the para nitro group afforded a 6-fold increase in kd. In contrast to thermal homolysis, the rate of photoinduced decomposition depends on both the extinction coefficient and the value of activation energy. Thus, nitro-containing alkylated verdazyls show the highest homolysis rate in both types of initiations. The achieved results afford a novel opportunity in the controlled generation of verdazyls and further application of these compounds in medicine and chemical industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...