Assessing electrochemical properties and diffusion dynamics of metal ions (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al and Zn) on a C2N monolayer as an anode material for non-lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
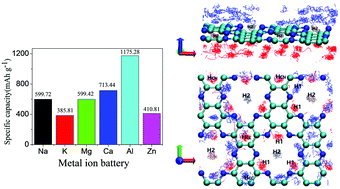
We perform first-principles molecular dynamics (FPMD) simulations together with a CI-NEB method to explore the structure, electrochemical properties and diffusion dynamics of a C2N monolayer saturated with various univalent, bivalent and trivalent metal ions. A characteristic irregular adsorption structure consisting of an inner coplanar layer at the large atomic pore and loosely bound outer layer is discovered for all six types of ions. The predicted specific capacities and mean open circuit voltages (OCVs) for them are: 600 mA h g−1, and 0.26 V (Na); 385 mA h g−1, and 1.56 V (K); 600 mA h g−1, and 0.96 V (Mg); 713 mA h g−1, and 1.31 V (Ca); 411 mA h g−1, and 1.40 V (Zn); 1175 mA h g−1, and 0.78 V (Al). For the energy favorable migration pathway, the diffusion energy barrier height for each ionic species is found to be 0.24 eV (Na+), 0.10 eV (K+), 0.25 eV (Mg2+) and 0.10 eV (Ca2+). The values are larger than 1.0 eV for both Zn2+ and Al3+. FPMD simulation at 400 K further predicted that the diffusion coefficients of Na and K atoms absorbed on the C2N monolayer are 5.33 × 10−9 m2 s−1 and 8.52 × 10−9 m2 s−1, respectively, which are one order of magnitude higher than those of other remaining ions discussed in our work. The C2N monolayer shows promising electrochemical properties and ion diffusion dynamics for use as the anode material in alkali metal ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...