Adsorption and activation of CO2 on Zrn (n = 2–7) clusters†
Abstract
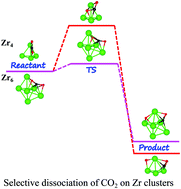
The first step in the conversion of CO2 to useful chemicals involves the adsorption of this molecule on a catalyst accompanied with its high degree of activation. In this paper, we explore the efficacy of small sized zirconium clusters, Zrn (n = 2–7), in the adsorption and activation of the CO2 molecule by using the density functional theory based ab initio method. The results of our calculations provide compelling evidence for the chemisorption and very high degree of activation of CO2 with the elongation of the C–O bond in the range of 1.27–1.42 Å compared to 1.16 Å for free CO2 and the deformation of the O–C–O bond angle from linear to 115–136°. This activation takes place through a charge migration from the Zrn cluster to the CO2 molecule resulting in the formation of CO2δ− species. To assess the catalytic potential of Zr-clusters for CO2 conversion, we also analyse the reaction pathways and the transition barrier heights for the dissociation of CO2 (CO2 → CO + O) on all the Zrn clusters. Our results for the dissociation of CO2 to CO and O fragments reveal that the transition barrier is small for all the Zrn clusters except for Zr2 and Zr4 and it attains a minimum value of 0.11 eV for an isomer of the Zr6 cluster. The present work clearly demonstrates that small-sized monometallic Zr-clusters are highly efficient in activating and dissociating a CO2 molecule adsorbed on these clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...