Decoupling between the translation and rotation of water in the proximity of a protein molecule†
Abstract
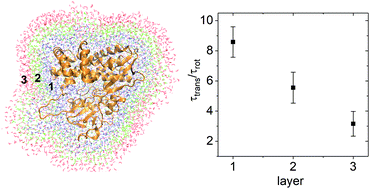
The interaction between water and biomacromolecules is of fundamental interest in biophysics, biochemistry and physical chemistry. By combining neutron scattering and molecular dynamics simulations on a perdeuterated protein at a series of hydration levels, we demonstrated that the translational motion of water is slowed down more significantly than its rotation, when water molecules approach the protein molecule. Further analysis of the simulation trajectories reveals that the observed decoupling results from the fact that the translational motion of water is more correlated over space and more retarded by the charged/polar residues and spatial confinement on the protein surface, than the rotation. Moreover, around the stable protein residues (with smaller atomic fluctuations), water exhibits more decoupled dynamics, indicating a connection between the observed translation–rotation decoupling in hydration water and the local stability of the protein molecule.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...