Effects of mixing between short-chain and branched-chain alcohols in protonated clusters†
Abstract
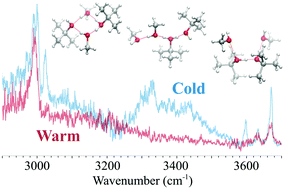
The previous analysis of the neat protonated branched-chain alcohol clusters revealed the impact of steric repulsion and dispersion of the bulky alkyl group on the hydrogen-bonded (H-bonded) structures and their temperature-dependence. To further understand the influence of the alkyl groups in H-bonded clusters, we studied the mixing of the two extremes of alcohols, methanol (MeOH) and tert-butyl alcohol (t-BuOH), with an excess proton. Infrared spectroscopy and a structural search of first principles calculations on the size-selected clusters H+(MeOH)m(t-BuOH)t (m + t = 4 and 5) were conducted. Temperature-dependence of the dominant H-bonded structures was explored by the Ar-tagging technique and quantum harmonic superposition approach. By introducing the dispersion-corrected density functional theory methods, it was shown that the effects of dispersion due to the bulky alkyl groups in the mixed clusters cannot be ignored for t ≥ 2. The computational results qualitatively depicted the characteristics of the observed IR spectra, but overestimation of the temperature-dependence with dispersion correction was clearly seen due to the unbalanced correction between linear H-bonded structures and compact cyclic ones. These results demonstrate the importance of extensive investigation and benchmarks on different levels of theory, and that a properly sampled structure database is crucial to evaluate theoretical models.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...