Kinetic selection of nonradiative excitation in photonic nanoparticles Gd2O3:Er
Abstract
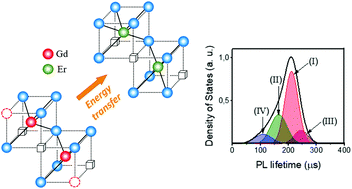
In the present work, we separate and classify four different pathways for UV-vis energy conversion with participation of Gd3+def and Er3+ ions located at dissimilar structural sites in the Gd2O3 lattice. The Gd3+def centers represent host cations with a distorted environment due to the nearest defects of the anionic sublattice. Two non-equivalent types of both Gd3+def donor and Er3+ acceptor centers occupying C2 and S6 structural sites are selected in Gd2O3:Er nanoparticles by the spectral-kinetic method. Such structural features provide the realization of several parallel channels of nonradiative Gd3+def → Er3+ energy migration and lead to a multimodal distribution of emission centers over the lifetime of the Er3+ excited states. The widths and the maxima of the kinetic parameter distributions depend on the degree of disorder in the nearest environment of Gd3+def donor centers. Our data show the possibility of practical realization of what is regarded as an additional pathway for the enhancement of excitation nonradiative transport in photonic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...