Catalytic performance of Pdn (n = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6) clusters supported on TiO2-V for the formation of dimethyl oxalate via the CO catalytic coupling reaction: a theoretical study†
Abstract
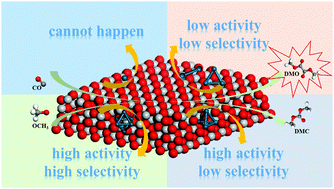
The formation of dimethyl oxalate (DMO) via CO catalytic coupling on a series of catalysts including Pdn (n = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6) clusters loaded on TiO2-V has been explored by density functional theory (DFT) calculation. The results show that different Pdn clusters have a remarkable influence on DMO formation. The Pd1/TiO2-V catalyst is not suitable for the CO catalytic coupling reaction since CO is easily bound to the O atom on the surface of TiO2-V leading to the formation of CO2. The activity of four catalysts complies with the following order of Pd4/TiO2-V > Pd6/TiO2-V > Pd2/TiO2-V > Pd3/TiO2-V by comparing the activation energy barriers of the rate-determining steps in the optimal paths. Charge analysis implies that less charge is transferred from the Pd4/TiO2-V and Pd6/TiO2-V catalysts to CO than on the other catalysts, which leads to the relatively weak adsorption of CO, and therefore CO has a greater tendency to react with other species on the surface. In addition, Pd6/TiO2-V also exhibits relatively higher selectivity toward DMO than the other three catalysts. Therefore, Pd6 is regarded as a suitable cluster, which is supported on TiO2-V demonstrating high catalytic activity and selectivity to DMO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...