Revealing the binding and drug resistance mechanism of amprenavir, indinavir, ritonavir, and nelfinavir complexed with HIV-1 protease due to double mutations G48T/L89M by molecular dynamics simulations and free energy analyses†
Abstract
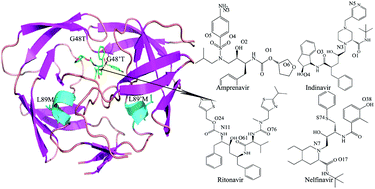
Infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) not only destroys the immune system bringing about acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), but also induces serious neurological diseases including behavioral abnormalities, motor dysfunction, toxoplasmosis, and HIV-1 associated dementia. The emergence of HIV-1 multidrug-resistant mutants has become a major problem in the therapy of patients with HIV-1 infection. Focusing on the wild type (WT) and G48T/L89M mutated forms of HIV-1 protease (HIV-1 PR) in complex with amprenavir (APV), indinavir (IDV), ritonavir (RTV), and nelfinavir (NFV), we have investigated the conformational dynamics and the resistance mechanism due to the G48T/L89M mutations by conducting a series of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and free energy (MM-PBSA and solvated interaction energy (SIE)) analyses. The simulation results indicate that alterations in the side-chains of G48T/L89M mutated residues cause the inner active site to increase in volume and induce more curling of the flap tips, which provide the main contributions to weaker binding of inhibitors to the HIV-1 PR. The results of energy analysis reveal that the decrease in van der Waals interactions of inhibitors with the mutated PR relative to the wild-type (WT) PR mostly drives the drug resistance of mutations toward these four inhibitors. The energy decomposition analysis further indicates that the drug resistance of mutations can be mainly attributed to the change in van der Waals and electrostatic energy of some key residues (around Ala28/Ala28′ and Ile50/Ile50′). Our work can give significant guidance to design a new generation of anti-AIDS inhibitors targeting PR in the therapy of patients with HIV-1 infection.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...