Photoreductive dissolution of cerium oxide nanoparticles and their size-dependent absorption properties†
Abstract
Cerium oxide has attracted attention recently for its photocatalytic properties, but there are gaps in understanding its performance, especially at low and high pH. UV irradiation of ceria nanoparticles causes electrons from photogenerated electron–hole pairs to localize as small polarons, yielding Ce3+ ions. In pH 10 solution, ceria nanoparticles capped with polyacrylic acid ligands can accumulate large numbers of Ce3+ defects as revealed by strong bleaching of the absorption onset. In contrast, we show that UV irradiation of several-nanometer diameter ceria nanoparticles in acidic (pH < 3) aqueous solution releases Ce3+ ions into solution with a quantum yield that approaches 70% and that varies with excitation wavelength, particle size, and the presence of a hole scavenger (glycerol) on the nanoparticle surface. The instability of Ce3+ at the nanoparticle surface and the ability of electron small polarons to migrate to the surface by hopping strongly suggest that nanoceria is fully oxidized and essentially free of Ce3+ centers at pH < 3. Efficient photoreduction and the excellent stability of unirradiated nanoparticles make it easy to shrink the nanoparticles using only light, while maintaining them in a fully oxidized state. This enables study of the size-dependent absorption properties of ceria nanoparticles that are free of Ce3+ defects. No evidence of quantum confinement is observed, consistent with highly localized excited states. The observed quantum yields of photoreduction are higher than reported for other metal oxides, revealing that a significant fraction of electron–hole pairs are available for driving surface redox reactions, even in fully oxidized particles.
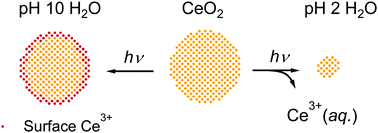


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...