Exploring fast water permeation through aquaporin-mimicking membranes†
Abstract
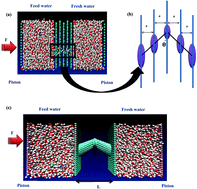
Using molecular dynamics simulations, herein, we illustrate that a bending structure shows different behaviors for fast water transport through aquaporin-mimicking membranes in multilayer graphene and tubular structures. This suggests that the bending structure enhances water transport through multilayer membranes, indicating the optimum state at θ = 45°. Disruption of the single-file water arrangement inside the membrane can contribute to promoting water transport in this system. However, a bending structure reduces the rate of water transport in tubular systems. Our results exhibit that a straight tubular membrane transfers water molecules faster than its non-straight counterpart. A stabilized form of the single-file water structure was observed in the membrane. Interestingly, we found that the tubular hourglass-shaped membranes possessed a lower free energy than the multilayer membranes with an hourglass shape. This can be attributed to the accommodation of the single-file water configuration in a confined space with hydrophobic characteristics. Accordingly, integrating an hourglass shape pore in a tubular structure in an impermeable membrane provides high water permeability compared with its multilayer counterpart. We also found that the wide variation in the dipole orientation of water molecules and the energy barrier have dominant effects in determining fast water transport through multilayer and tubular membranes, respectively. The contribution of interlayer spacing on fast water transport through multilayer membranes was also studied.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...