The effect of grain size on the hydration of BaZr0.9Y0.1O3−δ proton conductor studied by ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy†
Abstract
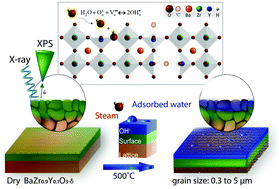
Three BaZr0.9Y0.1O3−δ (BZY10) pellets were prepared using different sintering processes, resulting in samples with different grain sizes, from 0.3 to 5 microns. Ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectra were recorded in argon, steam and oxygen atmospheres (100 mTorr) in the 300–500 °C temperature range. Deconvolution of O 1s peaks reveals 4 distinct contributions: sub-surface lattice oxide, termination layer oxides, OH− and gas-phase steam in wet environments. The OH− contribution of the O 1s peak includes sub-surface incorporation of protonic defects in the lattice related to hydration as well as surface hydroxylation and molecular water adsorption. The OH− concentration increases with grain size and with decreasing the analysis depth. These results suggest that grain boundaries associated with the larger grains adsorbed water more effectively. Thus, larger grains, which increase proton conductivity in BZY10, may also enhance catalytic activity for carbonaceous fuel oxidation by facilitating increased hydration and surface carbon removal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...