Selenium and sulfur inhomogeneity in free-standing ternary Sb2(Se,S)3 alloyed nanorods†
Abstract
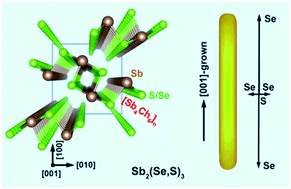
Composition engineering is an active topic of research for optical and electronic (nano)crystals and functional materials. We here demonstrate the control over the ratios and distributions of selenium and sulfur in ternary Sb2(Se,S)3 alloy nanorods (NRs), which were synthesized from a molecular chalcogen precursor, selenium disulfide (SeS2). By increasing the anion/cation precursor ratios (SeS2/SbCl3) from 0.5 : 1 to 1 : 1 and 1.5 : 1, an increase in both the Se fractions and the lengths × diameters of NRs is achieved with the Se and S distributions in Sb2(Se,S)3 varying from homogeneity to inhomogeneity. Within the inhomogeneous NRs obtained at high SeS2/SbCl3 ratios containing excessive chalcogen (Se + S), S decreases but Se increases from the center to the periphery as revealed by EDS elemental analyses performed on individual NRs. In particular, the 1D growth anisotropy of NRs allows for a large chalcogen concentration gradient along the axial direction of the resulting NRs from their middle to the two ends. Such non-uniform Se and S distributions can be rationally interpreted by analyzing the growth kinetics and processes of Sb2(Se,S)3 NRs and would give rise to uncommon (opto)electronic properties towards future nanowire-based devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...