Effects of pH and ions on the morphological evolution of boehmite prepared by hydrothermal treatment of ultrafine Bayer gibbsite
Abstract
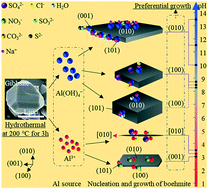
The desired morphology can improve the application and performance of boehmite and its subsequent products. Boehmite with various morphologies obtained by hydrothermal treatment of ultrafine Bayer gibbsite is systematically studied in aqueous solutions with pH of 3–13.5. Needle-like/long hexagonal, rhombic, and hexagonal boehmite with different crystallite sizes were formed in acidic, near-neutral, and alkaline solutions, respectively, which is mainly determined by the pH of the solution. Furthermore, ionic adsorption caused the differences in the exposed surface by reducing the surface energy, regulating the zeta potentials and altering the growth habits of boehmite. At pH of approximately 3, absorption of SO42− and Cl− anions on the (100) and (001) surfaces generated a fine needle-like shape, while absorption of NO3− on the (101), (100) and (010) surfaces formed a long hexagonal shape. At pH of approximately 8, SO42− and Cl− anions slightly enlarged the (010) area of rhombic boehmite with (101) and (010) exposed surfaces, and Na+ adsorption reduced the thickness of the (010) surface. In the pH range of 10 to 13.5, adsorption of SO32−, CO32−, and S2− anions formed hexagonal boehmite with (010), (101), and (100) exposed surfaces and affected the area of the (010) surface. Therefore, understanding the morphological evolution mechanism of boehmite can provide guidance for large-scale production of boehmite with desired morphology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...