Effect of dilution in a hydrothermal process and post-synthetic annealing on the tailoring of hierarchical ZnO nanostructures†
Abstract
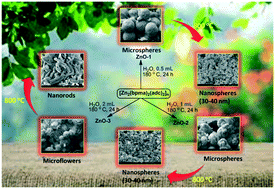
Using Zn(II) coordination polymers, namely [Zn2(bpma)2(adc)2]n, [Zn2(bpea)2(adc)2]n and {[Zn2(bpta)2(adc)2]·2H2O}n, as precursors, a variation in the morphologies and dimensionalities of the ZnO nanostructures is demonstrated through three operating parameters: presence of different sacrificial ligands in the precursor, volume of water in a hydrothermal reaction mixture (0.5, 1 and 2 mL) and post synthetic-annealing of hydrothermally grown nanostructures. For example, microspheres and microflowers (3D), nanosheets (2D) and nanotubes (1D) have been obtained with a change in the precursor and volume of water. The growth mechanism of these materials during the hydrothermal synthesis has been elucidated in detail. The dimensionality change from 3D microflowers to 1D nanorods upon further annealing is discussed. The formation of 1D nanotubes is also explained based on the difference in the growth of the different planes of ZnO. Their structural composition and surface morphology were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The XRD patterns have revealed that the as-synthesized ZnO nanostructures exhibit a hexagonal wurtzite phase. Based on the UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra, the band gap energies for the as-synthesized nanostructures ZnO-1 to ZnO-9 were found to be in the range of 3.01–3.24 eV. Further, the photoluminescence spectra of these nanostructures displayed the maximum absorption band within the range of 430–490 nm originating from the defect states of zinc interstitials, zinc vacancies and oxygen vacancies. Also, a diminishing effect on the emission intensities was observed as a result of decrease in the concentration of precursors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...