Effect of substitution on halide/hydrated halide binding: a case study of neutral bis-urea receptors†
Abstract
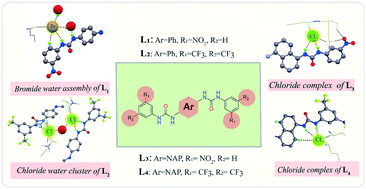
Four neutral dipodal receptors have been purposefully designed and synthesized by varying the substituents from a phenyl to naphthyl moiety to investigate the anion coordinating activities of bis-urea receptors. Crystal structure investigation of the complexes correctly validates the fact that the receptors L1–L4 form halide as well as hydrated halide complexes. Most interestingly in complex 2a, the phenyl based neutral bis-urea receptor L2 binds with two chloride ions via participation of N–H⋯Cl− interaction from the adjacent urea group and aromatic C–H⋯Cl− interaction along with the construction of a halide–water–halide bridged architecture supported by another identical receptor moiety. Meanwhile, another phenyl-based bis-urea receptor L1 binds to one bromide ion (1b) which is coordinated with two water molecules (from the lattice) forming a suitable 2 : 1 anion–receptor interaction. In all cases, the coordinated –NH protons from adjacent urea moieties play an important role in terms of coordination, and are oriented in a trans fashion with respect to the core substituent. The transformation from the phenyl to naphthyl ring shows a clear distinction in halide binding which is very much consistent with the size as well as hydrophobic nature of the substituent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...