Fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based DNA framework assembled split G-quadruplex nanodevices for microRNA sensing†
Abstract
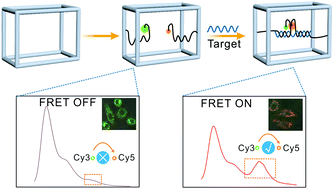
A DNA framework assembled split G4 nanodevice was fabricated to realize microRNA imaging in living HeLa cells. After hybridization with the target, the separated G4 segments underwent structural transformations, which could initiate fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) processes. Our design may pave a novel way to facilitate applications of the G4 motif.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...