Boosting the electrocatalysis of nitrate to nitrogen with iron nanoparticles embedded in carbon microspheres†
Abstract
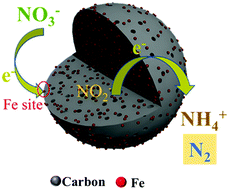
Human activities have increased the global nitrogen cycle imbalance, leading to serious water pollution. Inexpensive iron nanoparticles with large surface areas are in high demand in the field of environment restoration. Here, we report a hydrothermal method for the preparation of iron–carbon composites (Fe@C) with iron nanoparticles embedded in carbon microspheres. The resulting Fe@C catalyst shows a high nitrate conversion to nitrogen of 75.9% and a nitrogen selectivity of 98%. This study not only provides a simple strategy for the preparation of iron–carbon composites, but also boosts the practical application of Fe@C catalysts for water treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...