Metal catalyst-free photo-induced alkyl C–O bond borylation†
Abstract
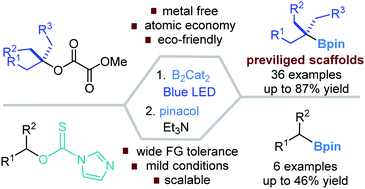
Metal catalyst free, blue visible light-induced C–O bond borylation of unactivated tertiary alkyl methyl oxalates has been developed to furnish tertiary alkyl boronates. From the secondary alcohols activated with imidazolylthionyl, moderate yields of boronates were attained under standard photo-induced conditions. Preliminary mechanistic studies confirmed the involvement of a (DMF)2–B2cat2 adduct that weakly absorbs light at 437 nm so as to initiate a Bcat radical. A radical-chain process is proposed wherein the alkyl radical is engaged.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...