Charge transfer from perovskite oxide nanosheets to N-doped carbon nanotubes to promote enhanced performance of a zinc–air battery†
Abstract
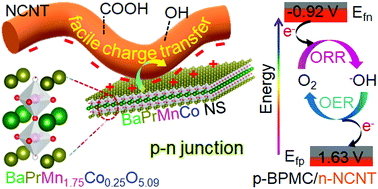
Room temperature engineered spatially connected p-type double perovskite oxide (BaPrMn1.75Co0.25O5+δ, BPMC) nanosheets (NSs) with n-type nitrogen-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes (NCNTs) show significant enhancement in bifunctional oxygen electrocatalytic activity. The optimization of the donor level by charge transfer from the perovskite to NCNTs is demonstrated to be a prodigious approach to facilitate redox oxygen activation. A proof-of-concept rechargeable zinc–air battery (ZAB) with BPMC containing a 10 wt% NCNT (BPMC/NCNT-10) cathode demonstrates the highest specific discharge capacity of 789.2 mA h gZn−1 and cyclic stability for 85 h at a current density of 5 mA cm−2.
- This article is part of the themed collection: (Photo)electrocatalysis for renewable energy


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...