Nanogel receptors for high isoelectric point protein detection: influence of electrostatic and covalent polymer–protein interactions†
Abstract
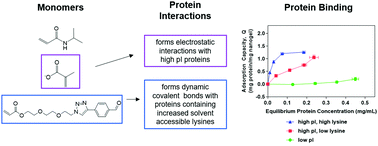
An aldehyde acrylate-based functional monomer was incorporated into poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) nanogels for use as protein receptors. The aldehyde component forms dynamic imines with surface exposed lysine residues, while carboxylic acid/carboxylate moieties form electrostatic interactions with high isoelectric point proteins. Together, these interactions effect protein adsorption and recognition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...