Sensitive RNase A detection and intracellular imaging using a natural compound-assisted tetrahedral DNA nanoprobe†
Abstract
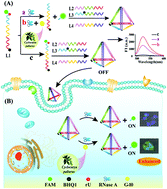
We report an intracellular imaging and assay nanoplatform for RNase A using a DNA tetrahedron-based fluorescent probe as a substrate. Importantly, a natural compound was used as an RNase A activity stimulator to improve the sensitivity. This platform provides an alternative for the diagnosis and prognosis of RNase A-related diseases and drug screening.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...