Porous hydrated ammonium vanadate as a novel cathode for aqueous rechargeable Zn-ion batteries†
Abstract
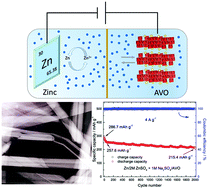
Development of suitable cathodes for use in aqueous rechargeable zinc ion batteries has attracted extensive interest. Herein, the electrochemical and structural changes of a novel porous hydrated ammonium vanadate (AVO) cathode in an aqueous ZnSO4-based electrolyte are reported. The AVO/Zn system exhibits a high reversible capacity of 418 mA h g−1, excellent long-term cyclability, and outstanding storage performance. Moreover, an interesting insertion mechanism with ternary carriers in a Zn/AVO aqueous rechargeable zinc-ion battery has been demonstrated for the first time.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...