Peptide nucleic acids harness dual information codes in a single molecule
Abstract
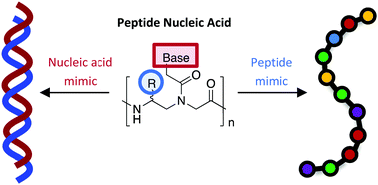
Nature encodes the information required for life in two fundamental biopolymers: nucleic acids and proteins. Peptide nucleic acid (PNA), a synthetic analog comprised of nucleobases arrayed along a pseudopeptide backbone, has the ability to combine the power of nucleic acids to encode information with the versatility of amino acids to encode structure and function. Historically, PNA has been perceived as a simple nucleic acid mimic having desirable properties such as high biostability and strong affinity for complementary nucleic acids. In this feature article, we aim to adjust this perception by highlighting the ability of PNA to act as a peptide mimic and showing the largely untapped potential to encode information in the amino acid sequence. First, we provide an introduction to PNA and discuss the use of conjugation to impart tunable properties to the biopolymer. Next, we describe the integration of functional groups directly into the PNA backbone to impart specific physical properties. Lastly, we highlight the use of these integrated amino acid side chains to encode peptide-like sequences in the PNA backbone, imparting novel activity and function and demonstrating the ability of PNA to simultaneously mimic both a peptide and a nucleic acid.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...