Experimental evidence of chalcogen bonding at oxygen†
Abstract
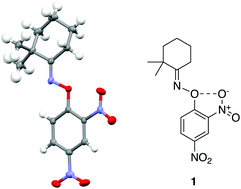
An o-nitro-O-aryl oxime was observed to exhibit a short O⋯O contact, which exhibited characteristics consistent with a chalcogen bond. The O–N bond length of the oxime was appreciably longer than the expected value, and NBO calculations indicated the presence of a n(O) → σ(O–N) orbital delocalisation. Topological analysis of the experimental electron density of two analogues shows the presence of a bond path between the two oxygen atoms, with ρ(r) and ∇2ρ(r) values consistent with an electrostatic interaction. Finally, electrostatic potential calculations indicate the presence of a σ-hole, the “smoking gun” indicating a Ch-bond. These results are unusual as oxygen is not typically considered to be a Ch-bond donor, especially in unactivated systems such as oximes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...