Defect formation-induced tunable evolution of oxygen functional groups for sodium storage in porous graphene†
Abstract
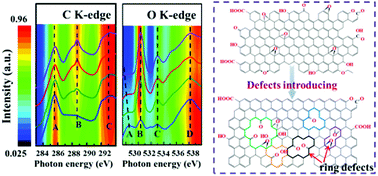
The coinciding effects of carbon defects and oxygen functional groups in porous graphene were demonstrated in this work. The species and distributions of oxygen functional groups evolved with the types of defects, especially those containing C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bonds mainly distributed along the edge of ring defects, and enhanced Na+ storage.
O bonds mainly distributed along the edge of ring defects, and enhanced Na+ storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...