Poly-γ-glutamic acid derived nanopolyplexes for up-regulation of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to augment tumor active targeting and enhance synergistic antitumor therapy by regulating intracellular redox homeostasis†
Abstract
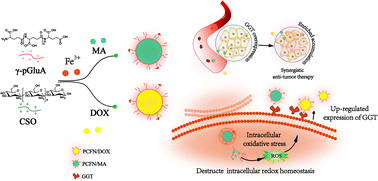
The active targeting strategy has achieved inspiring progress for drug accumulation in tumor therapy; however, the insufficient expression level of many potential receptors poses challenges for drug delivery. Poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-pGluA), a naturally occurring anionic biopolymer, showed high affinity with tumor-associated gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), which localized on the cell surface and exhibited intracellular redox homeostasis-dependent expression pattern; thus, GGT was utilized for mediating endocytosis of nanoparticles. Herein, GGT-targeting nanopolyplexes (γ-pGluA-CSO@Fe3+, PCFN) consisting of cationic chitosan and GGT-targeting γ-pGluA blended with iron ion were constructed to load reactive oxygen species-induced menadione (MA) and doxorubicin, which were utilized to investigate the mechanism of GGT up-regulation. Briefly, the pretreated PCFN/MA induced an intracellular oxidative stress environment, which facilitated adjusted up-regulated GGT expression and boosted tumor targeting. Subsequently, the destroyed redox homeostasis sensitized tumors for synergistic therapy. The innovative strategy of augmenting active targeting by disturbing intracellular redox homeostasis offers insight for the application of γ-pGluA-derived nanopolyplexes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...